Nissen Fundoplication
Information for patients
NHS Lanarkshire Nutrition and Dietetic Department
PIL.FUNDOP.19_28911.L
What is a Nissen Fundoplication?
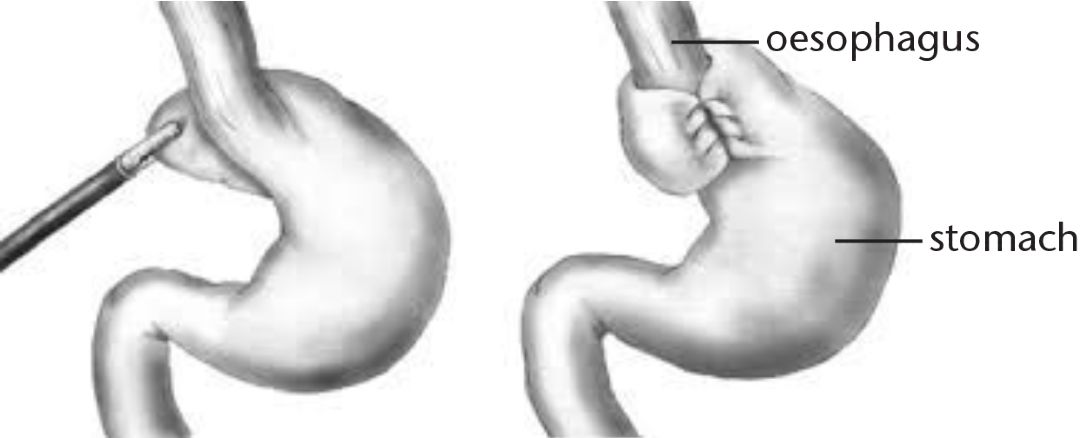
A fundoplication is a surgical procedure involving the stomach and oesophagus (the tube connecting your mouth to your stomach). It is used to treat severe gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD), where the acidic contents of the stomach are brought back into the oesophagus causing a burning sensation. This occurs because the join between your oesophagus and stomach is not working properly.
During the surgery, the top part of your stomach is wrapped around your oesophagus, tightening the join and preventing the stomach contents from refluxing. If there is a hiatus hernia present then this will be fixed at the same time.
If you undergo a corrective Heller’s Myotomy procedure, this can be accompanied by a fundoplication. Heller’s Myotomy procedure is usually performed if the muscles in your oesophagus do not relax and cause swallowing difficulty, this condition is called “achalasia”.
The speed of recovery from a fundoplication varies; however, most people are able to eat and drink normally three to six months after the procedure.
After the procedure
You will need to make some changes to your diet.
This information is only a general guide, if you are experiencing specific difficulties or have specific dietary requirements then please ask to be referred to a Dietitian.
You may experience some difficulty swallowing and burping, as well as bloating/ flatulence and pain/ discomfort after eating. These symptoms are normal and can last up to six weeks.
General Guidelines (for all stages)
- Eat little and often throughout the day (six to eight small meals) to ensure adequate nutrient intake and avoid feeling too full
- When eating, sit in an upright position and remain upright for at least 30 minutes after eating
- Relax, chew food well and eat slowly
- Drink small amounts of fluids with meals or use sauces to keep food moist
- To minimise burping, avoid drinking fizzy drinks, chewing gum and drinking through a straw.
- Limit foods that are gas-forming or irritating to the gut, such as: tomato products, caffeine, alcohol, onions, green peppers, beans, fatty foods, spicy foods, citrus fruits
- Avoid eating two hours before going to bed and sleep propped up with an extra pillow
- If you are struggling after advancing to the next stage of the diet, go back to the previous stage and continue to build-up your diet according to your tolerance
Stage 1: Liquid Diet (up to seven days)
This will begin in hospital and may last up to seven days. It aims to help minimise weight loss and prevent irritation to the site of your operation. Have small meals of liquids, make sure you drink slowly.
Examples of suitable fluids include:
- Water
- Diluting juice
- Fruit juice (apple, cranberry, grape, pomegranate juices)
- Smoothies (strained so that there are no seeds/pips)
- Smooth, blended soup
- Milky drinks
- Ice cream (allow it to melt in the mouth before swallowing)
- Decaffeinated tea
- Nutritional supplements (you will be provided with a seven-day supply to be taken twice per day)
Avoid
- Very hot or cold fluids
- Fizzy drinks (can cause bloating and gas)
- Alcohol
- Caffeine (limit if unable to exclude)
- Citrus juice
Stage 2: Soft/Moist Diet (Week 2-4)
This stage introduces food with a smooth, pureed texture to allow easier swallowing. Food should be smooth initially, moist and contain no lumps. You will need to use a blender, food processor or sieve to achieve this consistency and will need to add liquid in order to puree some foods. When adding liquid, try to use stock, gravy, cream, sauce, soup or fruit juice—water will dilute the nutrients but can be used if there is no suitable alternative.
Breakfast Ideas
- Smooth porridge
- Wheat biscuits soaked in milk
- Pureed fruit (tinned in syrup or juice)
- Full fat smooth yoghurt or fromage frais
- Eggs (scrambled, poached, soft omelette) pureed
Meal Ideas
- Puree cooked meat (add gravy/ sauce either before or after blending as needed) or fish with added white sauce, parsley/ cheese sauce
- Pulses such as lentils or chick peas can be added to curry sauce, soups and casseroles but limit these as they can cause gas and irritation
- Eggs (scrambled, poached, soft omelette) pureed
- Add grated/ cream cheese, yoghurt, whole milk, butter to sauces, soups, mashed potatoes/ sweet potato/ squash for extra nutrients.
- Creamy soup
- Vegetables cooked and mashed/ blended with butter, yoghurt, grated cheese, sauce and/ or full cream milk
- Soft pasta/ ground rice or grains pureed with a sauce or extra liquid.
Stage 2: Soft/Moist Diet (Week 2-4)
Pudding Ideas
- Milk Puddings like custard, rice pudding, semolina, tapioca
- Sponge cakes blended with cream or custard
- Mousse, milk jelly, Angel Delight®, blancmange
- Tinned or stewed fruit, blended with cream or custard
- Full fat smooth yoghurt, fromage frais, egg custard, crème caramel
Snack Ideas
- Soft biscuits or biscuits dipped in milk/ tea
- Corn based snacks such as. Skips®, Quavers®, cheese puffs
- Chocolates that can melt in the mouth
- Smoothies
- Milky drinks like hot chocolate, cafe latte, milkshake, Horlicks®, Ovaltine® – add extra cream or ice cream for additional calories
Stage 3: Soft Diet (Weeks 4-6)
You can proceed to a soft diet if you feel no pain or discomfort while following the pureed diet. Avoid any large, solid lumps and ensure that you chew your food well. Add extra sauce/liquid if required.
Meal ideas (in addition to puree foods)
- Shepherd’s Pie, Corned Beef Pie, Corned Beef Hash
- Cooked minced meats with gravy or sauce
- Small pieces of tender meat in casseroles, stews, hotpots
- Boneless fish poached in sauce, fish pie, Cullen skink
- Tinned tuna/ salmon (be cautious of small bones) with mayonnaise or sauce
- Cheese sauce dishes like cauliflower, macaroni, carbonara
- Mashed baked potato (no skin) with butter and a soft filling such as beans, cheese, tuna
- Mashed vegetables
- Mushy peas
- Snack ideas (in addition to puree foods)
- Cheese spread or cream cheese and digestive biscuits
- Marshmallows, soft jelly sweets
- Buttery crackers/ bread sticks dipped in cream cheese or houmous
- Soft fruits like raspberries, strawberries, ripe banana
- Tinned fruits
Avoid
The following foods can potentially become stuck in the oesophagus and should be avoided until the above diet is well-tolerated:
- Bread, rolls and sandwiches
- Dry foods like cold cuts of meat, crumbly cheese
- Stringy foods such as green beans, bacon, pineapple, orange
- Tough skins like jacket potato skins, crispy coatings
- Hard foods such as nuts, raw vegetables, salad, crisps
Stage 4: ‘Normal’ diet (Week 6 onwards)
If you have managed the soft diet well, you can slowly introduce a ‘normal’ diet as tolerated.
Further Information
You should be referred to see the diabetes dietitian for further information and individual advice.
Community Nutrition Support Dietitians
14 Beckford Street, Hamilton ML3 0TA
Tel: 01698 754800
NHS Lanarkshire – for local services and the latest health news visit
NHS Lanarkshire General Enquiry Line: 0300 30 30 243
NHS inform – The national health information service for Scotland.
Tel No: 0800 22 44 88
Pub. date: November 2023
Review date: November 2025
Issue No: 03
Reference: PIL.FUNDOP.19_28911.L
23_25483
If you need this information in another language or format, please e-mail:





